Complement Factor B (CFB) is a critical component of the alternative complement pathway, one of the three complement system pathways essential for innate immunity. It plays a central role in boosting immune responses by forming the C3 convertase enzyme complex. Excessive activation of CFB, however, has been linked to various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), and C3 glomerulopathy. These connections have driven significant research into targeting CFB therapeutically, positioning the Complement Factor B Inhibitor Market as a rapidly advancing sector in immunology and precision medicine.
The Biological Role of Complement Factor B
CFB is a serine protease that binds to complement component C3b, forming the C3bB complex, which Factor D cleaves into Bb and Ba fragments. The Bb fragment remains attached to C3b, generating C3 convertase (C3bBb), a pivotal enzyme that amplifies complement activation. This cascade enhances immune responses and inflammation. While vital for pathogen defense, uncontrolled activation may cause tissue damage and chronic inflammation, making CFB modulation an appealing therapeutic approach to manage complement-mediated disorders without fully suppressing immune function.
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Factor B
Hyperactivation of the alternative complement pathway contributes to several inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. In AMD, complement-driven inflammation harms retinal cells, causing vision deterioration. In aHUS and C3 glomerulopathy, dysregulation results in kidney injury. Inhibiting Factor B prevents the formation of the C3 convertase complex, reducing complement amplification and inflammation. This targeted intervention maintains immune equilibrium while minimizing the infection risks associated with broader complement inhibition.
Drug Development and Research Advances
Pharmaceutical companies have identified CFB inhibition as a promising therapeutic strategy. Multiple drug modalities, including small molecules, monoclonal antibodies, and RNA-based therapies, are under development. Preclinical studies demonstrate that CFB inhibition can significantly lower complement activation markers and improve disease outcomes. Several CFB Inhibitor Drugs have progressed to preclinical and clinical evaluation, marking milestones in immunotherapy innovation.
Clinical research primarily focuses on complement-mediated kidney and ocular diseases. The advancement of these studies is closely monitored globally, as favorable outcomes could drive regulatory approvals and market adoption. This underscores the importance of CFB Inhibitor Clinical Trials in validating both safety and efficacy of emerging therapies.
Key Players and Industry Landscape
Growing interest in complement biology has prompted numerous biotechnology and pharmaceutical firms to explore Factor B-targeted therapeutics. Both established and emerging companies are investing in research programs to develop next-generation inhibitors. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and collaborations are accelerating discovery, optimizing clinical testing, and streamlining regulatory approaches. The increasing number of CFB Inhibitor Companies highlights a competitive and innovative market leveraging advanced technologies like AI-driven modeling and structure-based drug design to enhance potency, specificity, and safety.
Evolution of CFB Inhibitor Drugs
The development of CFB Inhibitor Drugs has evolved from conventional small molecules to biologics and gene-silencing agents. Small molecules target Factor B’s active site, providing oral convenience and systemic efficacy, while monoclonal antibodies and RNA therapeutics offer targeted, high-specificity inhibition. Clinical evidence suggests that Factor B inhibitors could address both rare complement disorders and more common conditions like diabetic nephropathy and dry AMD. Ongoing research is focused on improving pharmacokinetics, reducing immunogenicity, and ensuring long-term safety.
Market Trends and Drivers
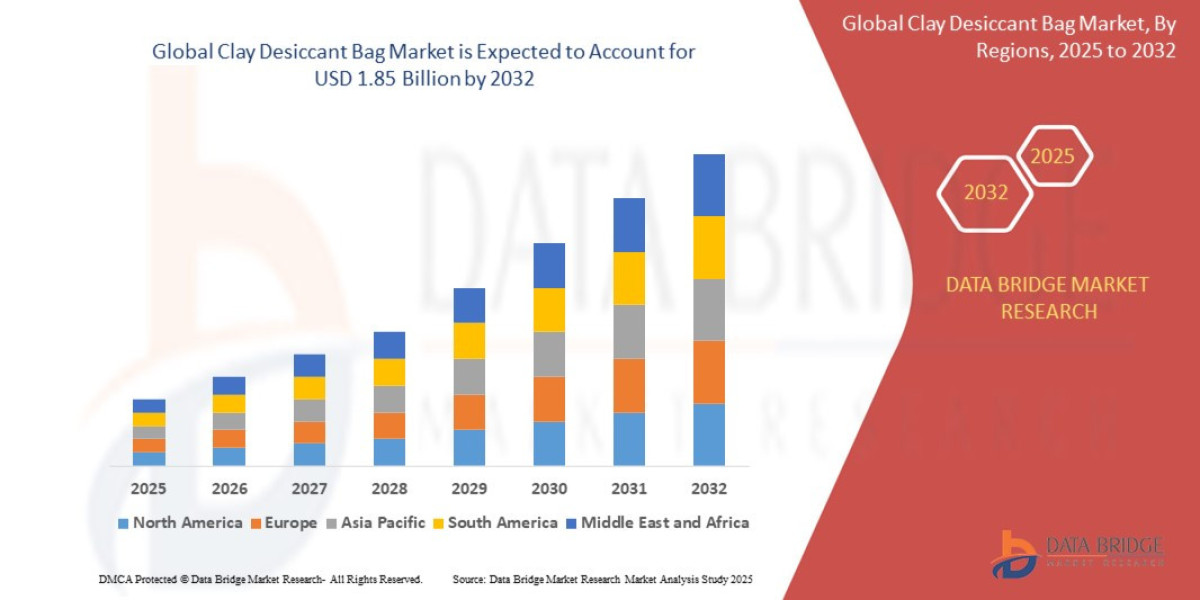
The global CFB Inhibitor Market Size is projected to grow significantly over the next decade due to increased awareness of complement-mediated disorders, rising investments in immunology research, and technological advancements in biologics. The prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases, coupled with unmet therapeutic needs, is driving demand. Expansion of genetic screening and biomarker-based diagnostics allows for early identification of patients suitable for CFB-targeted therapy. Strong regulatory backing and precision medicine initiatives further support market growth.
Future Outlook
Industry forecasts indicate that the CFB Inhibitor Market Forecast will show consistent revenue growth as multiple drug candidates advance through late-stage trials. Successful commercialization of Factor B inhibitors is expected to transform treatment options for complement-mediated diseases. Market growth will also benefit from academic-industry collaborations, enhanced R&D funding, and favorable patent landscapes. Personalized medicine approaches will further increase demand for complement inhibitors tailored to specific genetic profiles.
Challenges
Despite promising prospects, developing CFB inhibitors faces challenges, such as maintaining an optimal balance between complement suppression and immune protection. Over-inhibition could increase infection risk or compromise immune surveillance. Other hurdles include identifying reliable biomarkers to monitor therapy, the high cost of biologics, and the technical complexity of complement assays. Rigorous clinical design, pharmacovigilance, and technological innovation are essential to address these issues.
Conclusion
Complement Factor B remains a pivotal target for modulating immune responses, offering potential therapies for a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. As clinical evidence and market interest grow, CFB Inhibitor Drugs are poised to reshape treatment strategies for complement-related disorders. Continued research, strategic partnerships, and regulatory progress will determine the pace at which these therapies reach patients and achieve their full therapeutic potential.
Latest Reports by DelveInsight:
Critical Limb Ischemia Market | Cystic Fibrosis Market | Deep Brain Stimulation Market | Degenerative Disc Disease Market | Dementia Market | Diabetes Market | Diabetic Foot Ulcers Market | Diabetic Gastroparesis Market | Digestive System Fistula Market | Dilators Market | Dravet Syndrome Market | Drug Hypersensitivity Market | Dry Eye Disease Market | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Market | Edward's Syndrome Market | Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Market | Encephalitis Market | End-Stage Renal Disease Market | Energy Based Aesthetic Devices Market | Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis Market | Epithelioid Sarcoma Market | Erosive Hand Osteoarthritis Market | Erythromelalgia Market | Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy Market
About DelveInsight
DelveInsight is a leading Business Consultant, and Market Research firm focused exclusively on life sciences. It supports Pharma companies by providing comprehensive end-to-end solutions to improve their performance. It also offers Healthcare Consulting Services, which benefits in market analysis to accelerate the business growth and overcome challenges with a practical approach.
Media Contact
Company Name: DelveInsight Business Research LLP
Contact Person: Abhishek kumar
Email: [email protected]
City: Albany
State: New York
Country: United States
Website: https://www.delveinsight.com